1.What is a Hi-Pot Test?
Definition and Basic Principles
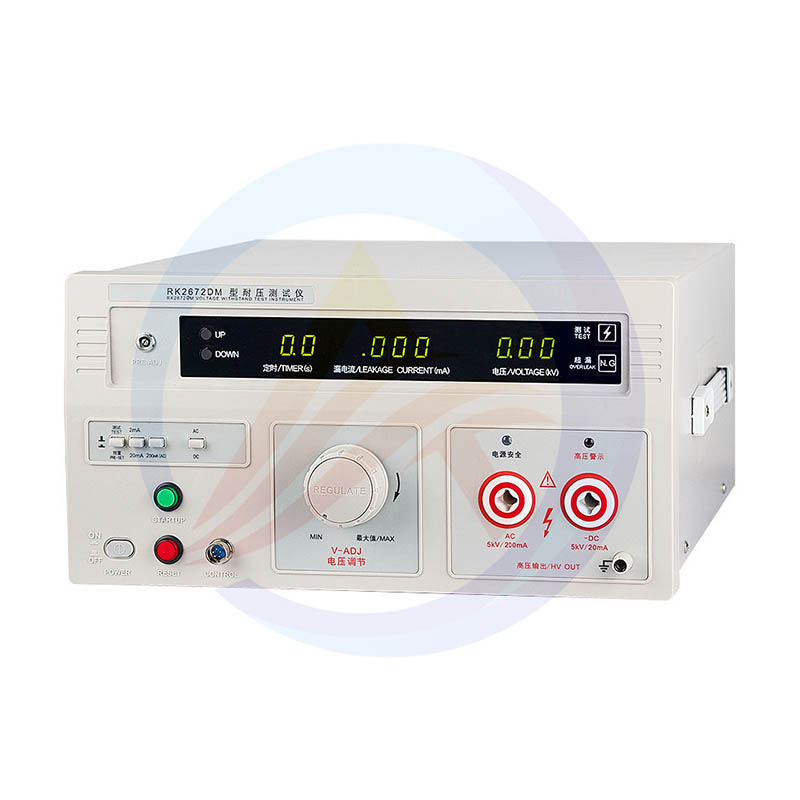
The Hi-Pot Test (High-Potential Test or withstand voltage tester) is a non-destructive electrical safety test used to verify the insulation integrity of electrical equipment or components. By applying a voltage significantly higher than the device’s rated operating voltage (typically 2× the working voltage + 1000V) for a specified duration (e.g., 1 minute), the hi-pot test detects insulation defects such as excessive leakage current or breakdown.
Key Objectives:
lEnsure insulation does not fail under high-voltage conditions, preventing electric shock or short circuits.
lValidate manufacturing quality by identifying latent defects (e.g., micro-voids, cracks, or contaminants in insulation materials).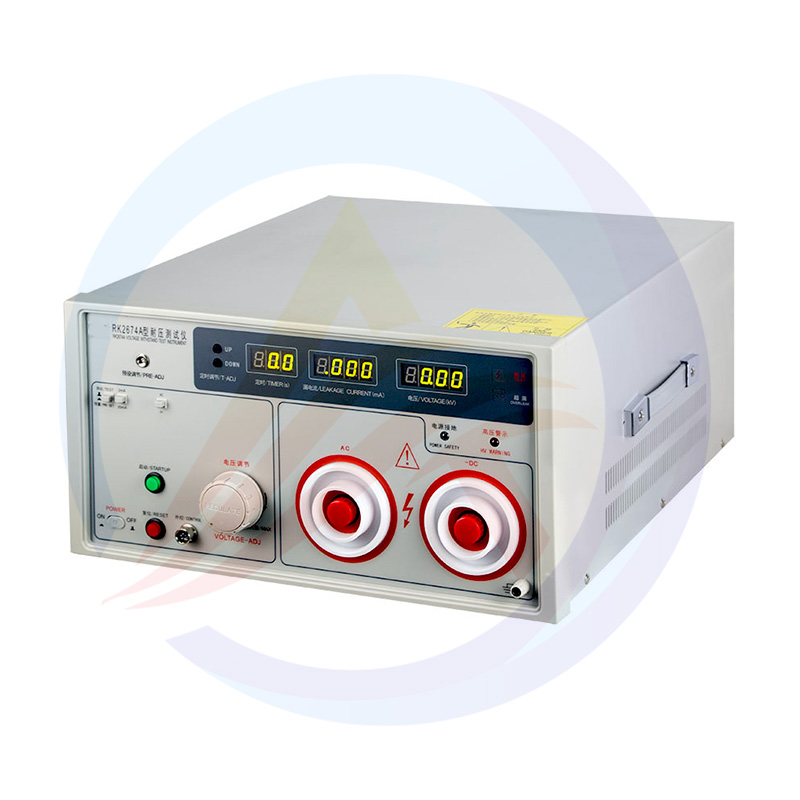
2.The Role and Necessity of Hi-Pot Testing
Why is Hi-Pot Testing Essential?
(1) Ensuring User Safety
lElectric Shock Prevention: Tests insulation materials’ ability to withstand high voltages, preventing leakage during abnormal conditions.
lFire Risk Mitigation: Avoids arcing or short circuits caused by insulation failure.
(2) Compliance Requirements
lInternational Standards:
IEC 60601 (Medical Devices): Requires withstand voltage ≥1500V AC.
UL 60950 (IT Equipment): Test voltage = 1000V AC + 2× rated voltage.
ISO 26262 (Automotive Electronics): Mandates Hi-Pot testing for all high-voltage components.
(3) Improving Product Quality
lEarly Defect Detection: Identifies assembly errors (e.g., insufficient conductor spacing) or material flaws (e.g., uneven insulation thickness).
lReducing Post-Market Risks: Lowers recall costs due to insulation failures (products failing Hi-Pot tests have a 300% higher recall rate).
3.Common Hi-Pot Test Failures and Solutions
(1)Root Cause Analysis
Failure Type | Possible Causes | Solutions |
Excessive Leakage | Contaminated/aged insulation | Clean or replace insulation |
Instant Breakdown | Insufficient conductor spacing | Redesign PCB layout |
Data Fluctuations | High humidity (>60% RH) | Test in climate-controlled labs |
(2)Safety Precautions
Operator Protection: Use safety shields and high-voltage warnings.
Equipment Calibration: Calibrate testers every 6 months (error <±3%).
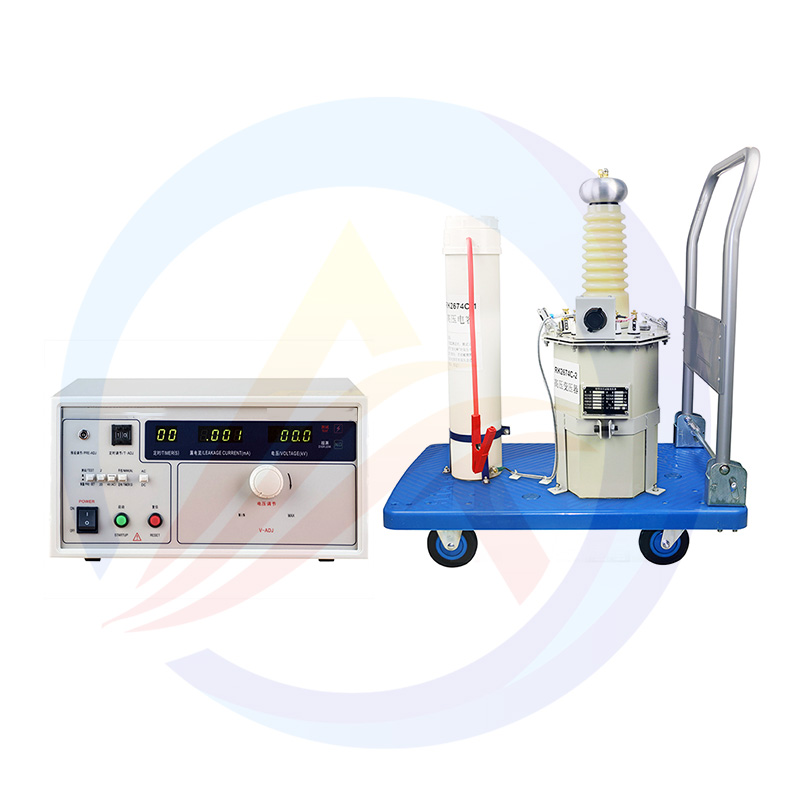
4.Hi-Pot Tester Selection Guide
(1)Key Parameter Comparison
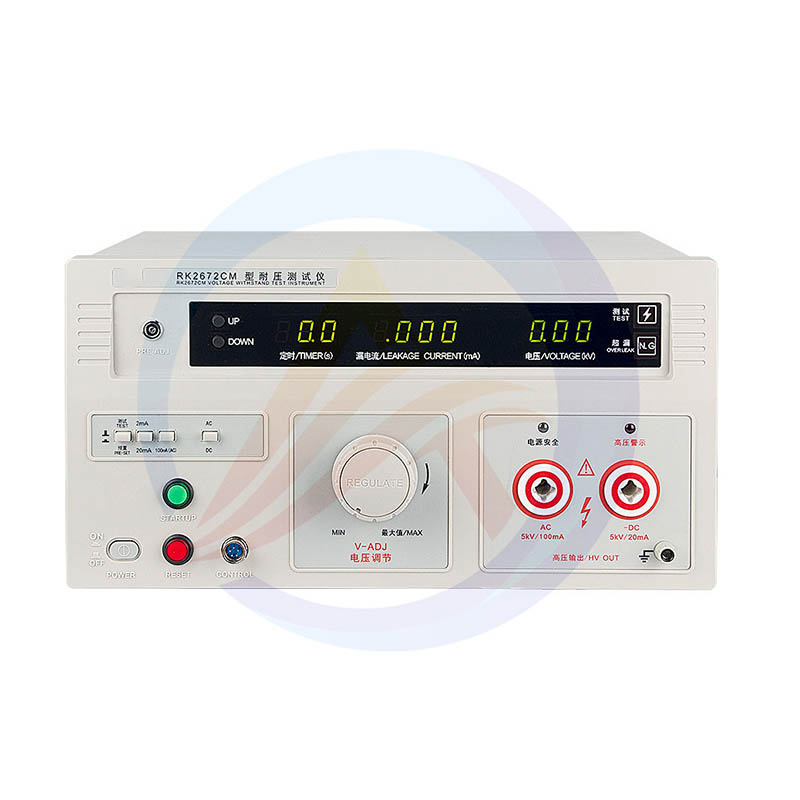
Model | RK2670AM | RK2672AM | RK2672BM | RK2672CM | RK2672DM | RK2672DF | |
AC | Voltage output | 0~5kV | |||||
Testing Current | 0~2/20mA | 0~2/20/100mA | 0~2/20/200mA | ||||
DC | Voltage output | / | 0~5kV | / | 0~5kV | / | |
Testing Current | / | 0~2/10mA | / | 0~2/20mA | / | ||
Test precision | ±5% | ||||||
Test time | 0.0s~999s 0.0=continuous testing | ||||||
Transformer capacity | 100VA | 500VA | 1000VA | ||||
PLC Interface | Optional | ||||||
Power | AC:220V±10% 50Hz/60Hz±3Hz | ||||||
Work environment | Temperature:(0-40)℃ ; Humidity ≤75%RH | ||||||
Dimension(DxWxH) | 320*270*180mm | 320*280*180mm | 407*378*193mm | ||||
Weight | 9.75Kg | 10.1kg | 14.4kg | 20.1kg | 24.8kg | 24.2kg | |
Spare parts | High voltage test line, high voltage rod, grounding wire, power cord | ||||||
Optional | RK8N+, PLC interface, RK-16G, RK101 voltage withstand point inspection box | ||||||
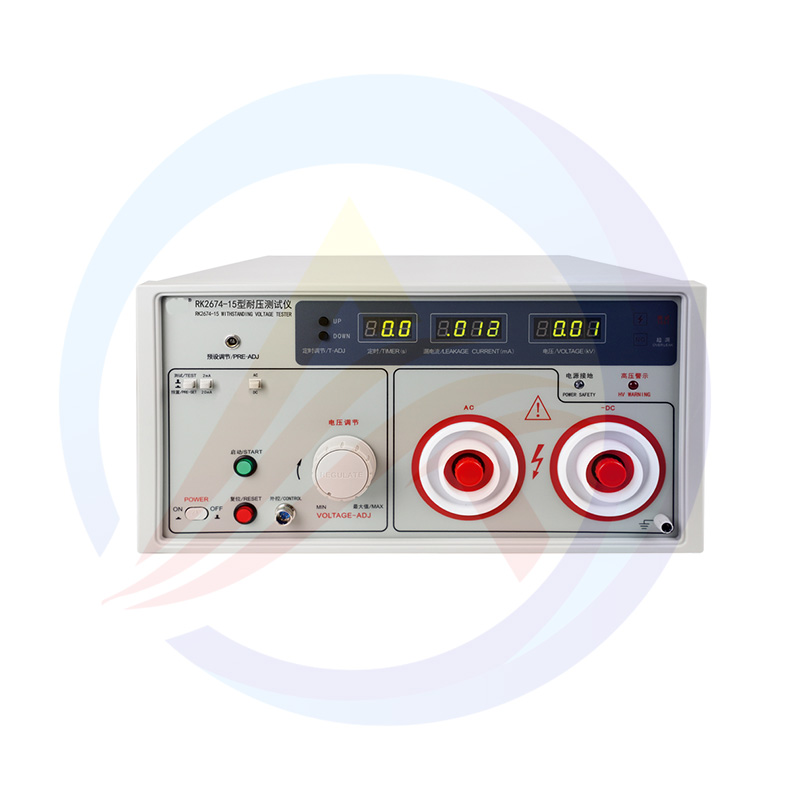
Model | RK2674-15 | RK2674-AC20 | RK2674A | RK2674B | RK2674C | |
AC | Voltage output | 0~15kV | 0~20kV | 0~30kV | 0~50kV | |
Testing current | 0~2/20mA | 0~2/20/40mA | ||||
DC | Voltage output | 0~15kV | / | 0~20kV | 0~30kV | 0~50kV |
Testing current | 0~2/20mA | / | 0~2/10mA | 0~2/20mA | ||
Test precision | ±5% | |||||
Test time | 0.0s~999s 0.0=continuous testing | 1~999s±1% | 1~99s±1% | |||
Transformer capacity | 300VA | 400VA | 600VA | 2000VA | ||
PLC Interface | Optional | None | ||||
Power | AC220V±10% 50Hz/60Hz | 220V±10% 50Hz/60Hz | AC220V±10% 50Hz/60Hz | |||
work environment | Temperature:(0-40)℃ ; Humidity≤75%RH | |||||
Style | Desktop | Cabinet type | Disconnect-type | |||
Dimension | 432*492*225mm | 539*650*930mm | ⑴375*279*196mm | |||
Weight | 33.4KG | 27.75Kg | 33.44KG | 68.84kg | ⑴12.05Kg ⑵63.14kg | |
Spare Parts | High voltage test line, grounding wire, power line | High voltage test line, grounding wire, power line, high voltage discharge rod, connecting wire | ||||
Optional | RK101 series inspection box | |||||
(2)Recommended Models:
Mid-Range: AOT-RK2672
Industrial: AOT-RK2674
5.Future Trends in Hi-Pot Testing
Technological Innovations
Smart Testing: AI algorithms analyze leakage current waveforms to predict insulation lifespan (e.g., Keysight’s PathWave).
Contactless Testing: Electromagnetic induction for non-physical testing (under development).
Energy Efficiency: Power recovery systems reduce test energy consumption by 70%.

6.Conclusion: The Indispensable Hi-Pot Test
Hi-Pot testing is the final safeguard for electrical safety. Whether meeting regulations, reducing recalls, or enhancing brand trust, rigorous Hi-Pot testing is critical.
Action Steps:
Upgrade test equipment to comply with latest standards (e.g., IEC 62368-1:2023).
Train staff with certifications like IPC-A-600.