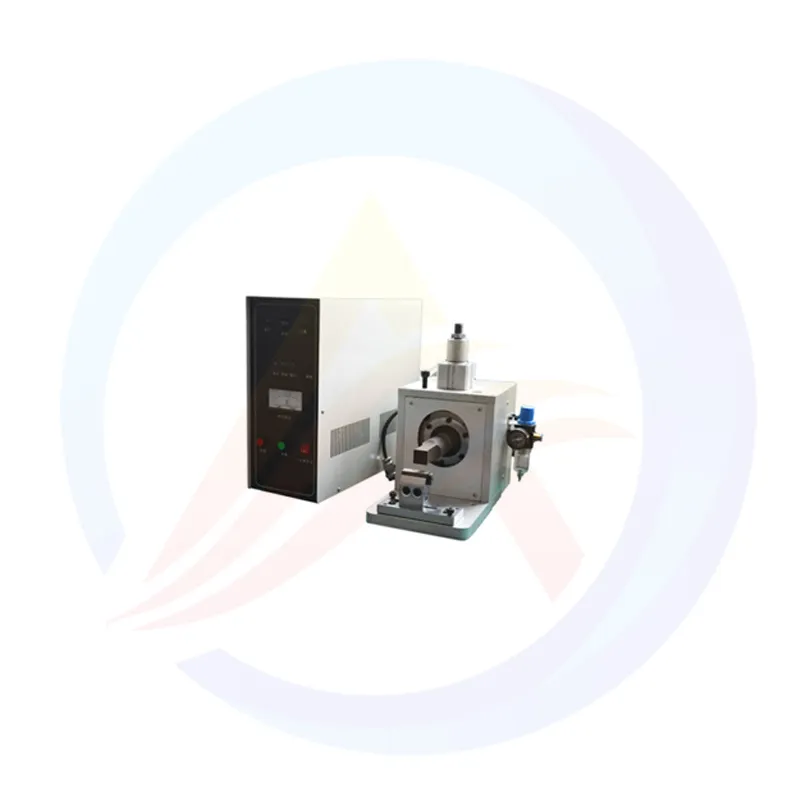
With the rapid development of new energy storage technologies, lithium-ion battery manufacturing quality directly determines its energy density, cycle life, and safety. Among battery component connection processes, ultrasonic welding has become a core solution for tab and electrode assembly bonding, thanks to non-thermal damage, high bonding strength, and stable process control.
1. Introduction
In new energy vehicles and energy storage systems, the demand for high-performance lithium-ion batteries has raised higher requirements for the reliability and consistency of internal component connections. Traditional welding methods like resistance and laser welding face issues such as excessive heat input, which damages diaphragms, melts tabs, or increases joint internal resistance, limiting battery performance.
Ultrasonic welding achieves solid-state bonding via high-frequency mechanical vibration, avoiding external heat sources and solving thermal damage to sensitive components. Advanced ultrasonic welding equipment integrates precision control and high-performance structures, adapting to different battery materials and structures. This paper explores its technical characteristics and application effects to support battery manufacturing optimization.
2. Core Technical Characteristics of Ultrasonic Welding Equipment
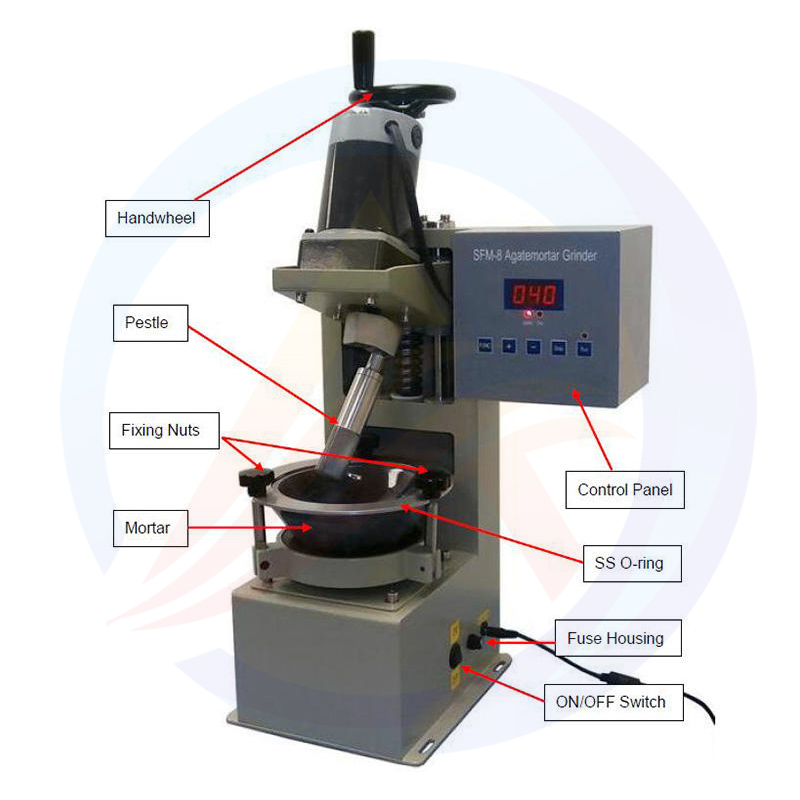
2.1 Precision Control System
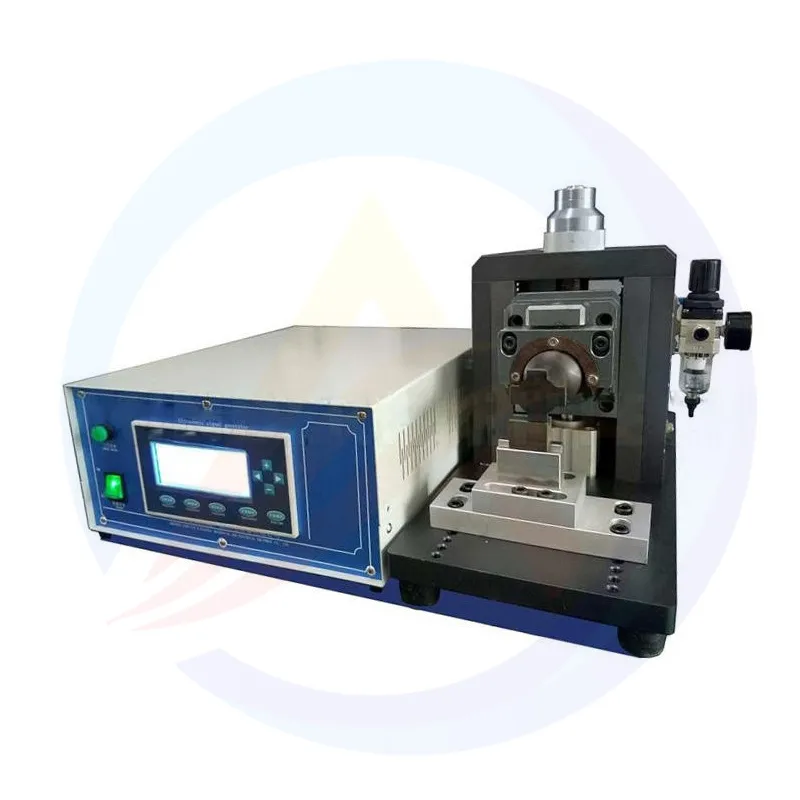
The equipment adopts a microprocessor-based integrated control circuit for real-time welding monitoring and adjustment. Its automatic frequency tracking function dynamically compensates for deviations caused by component temperature changes or wear, keeping the vibration frequency in the optimal range, ensuring stable energy transmission and avoiding waste or overheating.
In parameter adjustment, it supports flexible setting of preloading time, welding time, output power, and pressure holding time. The user-friendly human-machine interface, with anti-interference coding, prevents parameter errors from electromagnetic interference, ensuring process stability in industrial environments.
2.2 High-Stability Mechanical Structure
High-precision guideway components ensure stable linear motion during welding head pressure application and vibration transmission, reducing position deviation from mechanical vibration, ensuring uniform welding force, and avoiding tab deformation from stress concentration.
The welding head, made of high-hardness alloy and processed by high-precision grinding, has a surface pattern that enhances friction for sufficient energy transfer and offers excellent wear resistance, maintaining consistent welding quality in long-term mass production.
2.3 High-Performance Component Configuration
Core components ensure overall reliability. The energy conversion system uses high-quality ceramic chips with high electroacoustic conversion efficiency, reducing energy loss when converting electrical to mechanical vibration energy. Structural supports like aluminum bars are made of high-strength materials, avoiding deformation under long-term high-frequency vibration.
The control system is equipped with high-performance single-chip microprocessors, processing multi-channel sensor signals (pressure, frequency, time) in real time for closed-loop welding control, ensuring each cycle follows set parameters and improving joint consistency.
3. Parameter Adaptation to Lithium-Ion Battery Materials
3.1 Welding Parameter Matching for Different Tabs
The equipment adapts well to different tabs. For cathode tabs (5-10 layers of 20μm aluminum foil + 0.1mm pure aluminum tabs), adjusting welding time (0.05-2s) and output power achieves reliable bonding. Typical forms include 3×4mm three-point welding (25mm length) or 3×25mm linear welding, with high peeling strength and no cracks.
For anode tabs (5-10 layers of 10μm copper foil + 0.1mm pure nickel tabs), based on copper’s high thermal conductivity and hardness, adjusting power and pressure avoids virtual or over-welding, ensuring low internal resistance and stable conductivity.
3.2 Welding for Composite Materials and Cover Plates
It meets the needs of composite materials and cover plates. In Al-Ni composite belt welding with aluminum cover plates/shell bottoms, it completes two groups of 3×3mm (10mm length) or 3×4mm (14mm length) solder joints, and flexibly sets solder points (6 or 9 per group) to ensure sealing and stability.
For 0.1mm aluminum strips and 1-3mm aluminum cover plates, short welding time and moderate power realize 3×3mm/3×4mm single-point welding or 3×3mm double-point welding (8mm length), with no cover plate melting or deformation and good airtightness.
4. Practical Welding Performance and Quality Advantages
4.1 Excellent Welding Quality
In practice, the equipment ensures good welding quality with solid joints, no virtual/missing welding, and no vibration powder, avoiding internal short circuits. The welding area temperature is below the diaphragm/insulation material melting point, preventing burning or deformation. Reasonable parameters prevent tab/electrode cracking, ensuring internal structure integrity.
4.2 Adaptability to Mass Production
Under long-term mass production, high-wear-resistant welding heads and reliable components maintain consistent quality. The control system’s anti-interference and parameter memory functions enable quick model switching, reducing adjustment time. The high-efficiency energy conversion system reduces power consumption, and modular components simplify maintenance. A complete after-sales system (warranty, lifetime support) guarantees production continuity.
5. Conclusion
Ultrasonic welding is key to improving battery quality and efficiency. The equipment, with precision control, stable structure, and high-performance components, adapts to different materials and structures, solving traditional welding bottlenecks with solid joints, no thermal damage, and no powder.
In the future, with high-energy-density batteries (e.g., solid-state batteries), demands for precision, material compatibility, and intelligent control will increase. Optimization will focus on improving frequency stability, expanding material scope, and integrating intelligent monitoring to support the lithium-ion battery industry’s sustainable development.