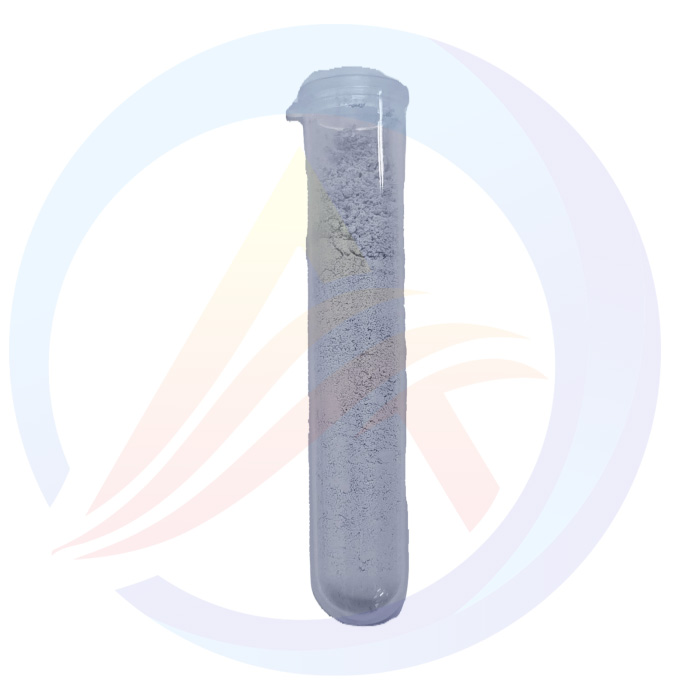
This is a micro-nano-scale prussian blue-like material, mainly used in sodium-ion batteries.
Specification:
Project | Technical indicators | Typical value | Unit | Testing method/specification |
Packaging | The packaging is tight and undamaged | Qualified | / | Visual estimation |
Appearance | Blue powder, no lumps | Qualified | / | Visual estimation |
Particle size | D10 | ≥2.0 | 2.189 | μm | BT-9300ST Laser particle size analyzer |
D50 | 5 ±0.5 | 4.935 | μm |
D90 | ≤10 | 8.550 | μm |
Dmax | ≤20.0 | 10.83 | μm |
Bulk density | ≥0.4 | 0.4192 | g/cm3 | BT-301 Tapped density tester |
Tapped real density | ≥0.7 | 0.7662 | g/cm3 |
Compaction density | ≥1.6 | 1.6700 | g/cm3 | True density analysis instrument |
Water content | ≤5 | 4.29 | % | Mead Halogen moisture meter (120℃) |
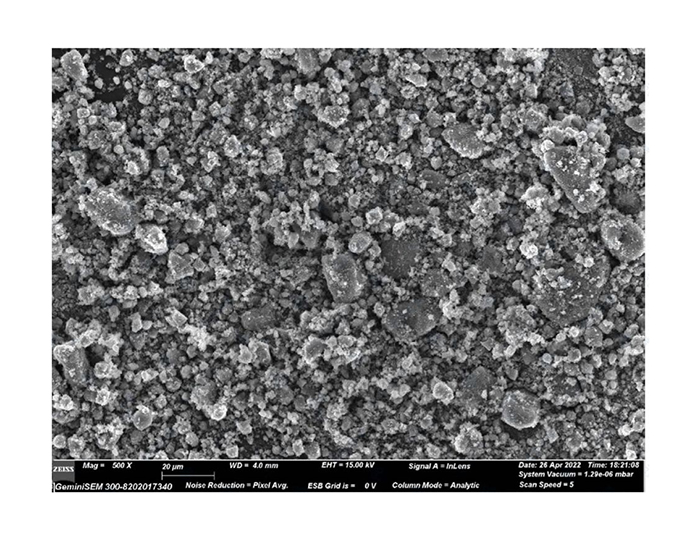
SEM | Cube | Cube | / | Scanning electron microscope |
100mA/g | Charging gram capacity | ≥140 | 151.91 | mAh/g | Half-battery At 25℃ |
Discharge gram capacity | ≥140 | 151.75 | mAh/g |
The first Coulomb efficiency | ≥95 | 99.90 | % |
Storage conditions | The product is prone to absorbing water. For long-term storage, it should be placed in a glove box |


Exhibition


Cerificate
Q1:What is a Prussian blue?
A:Prussian blue is used as a positive electrode material for batteries. Its structure contains an open framework, which is conducive to the intercalation/deintercalation of lithium ions and has a relatively high theoretical specific capacity. Through modification (such as introducing potassium ions and regulating crystalline water), the cycling stability and ion conductivity can be enhanced, which has application potential in low-cost and environmentally friendly potassium/sodium-ion batteries and is one of the research hotspots of new battery materials.
Q2:The main function of Prussian blue powder
A:Prussian blue open frame structure allows for rapid intercalation/deintercalation of ions, achieving charge storage and release.Enhancing performance: Through modification (such as adjusting the crystalline water and introducing heteroatoms), the cycling stability, ionic conductivity and specific capacity can be optimized.
Q3:The usage method of Prussian blue
A: The usage steps of Prussian blue powder for batteries: First, pre-treat, screen the powder evenly, wash and dry to regulate the crystalline water; Refabricate the electrode, dissolve it with conductive agents and binders in solvents to form a slurry, coat it with current collectors such as aluminum foil, and then dry and roll it. Finally, assemble the battery, and combine it with the negative electrode, separator, and compatible electrolyte (potassium/sodium system) to form a button or pouch battery. After liquid injection and sealing, it is activated and used after formation.
Q4:How to choose Prussian blue
A: Purity and crystalline water: High purity reduces side reactions. The content of crystalline water affects ion conduction and needs to be matched with the requirements of the battery system.
Particle size distribution: Uniform particle size is conducive to the dispersion of the slurry. Fine particles (nanometer level) can enhance the reactivity but increase the internal resistance.
Modification process: Products that have been modified by potassium ion doping, surface coating, etc. are preferred to enhance cycling stability and conductivity.