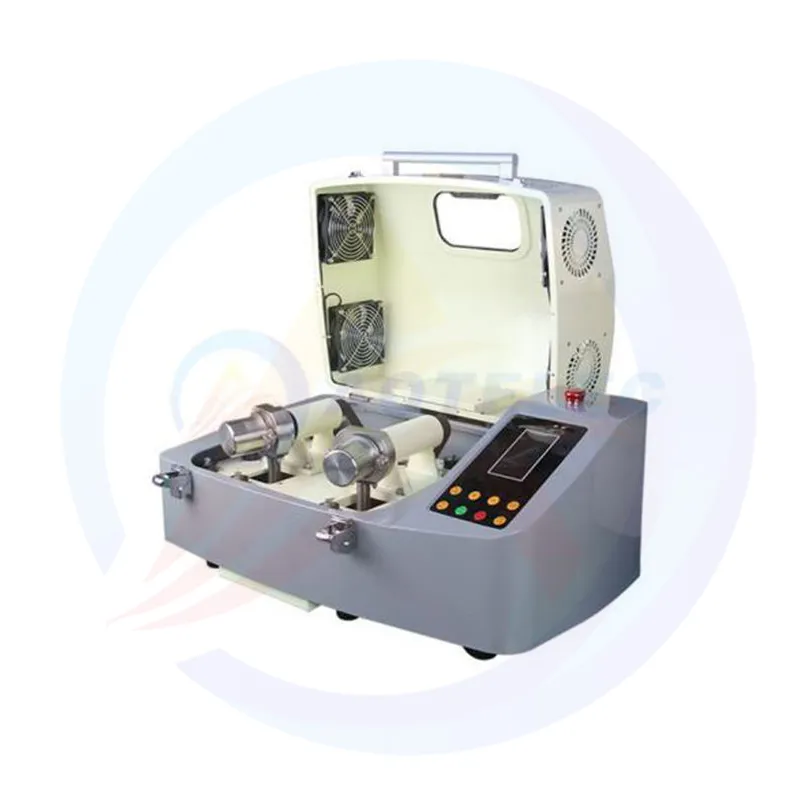
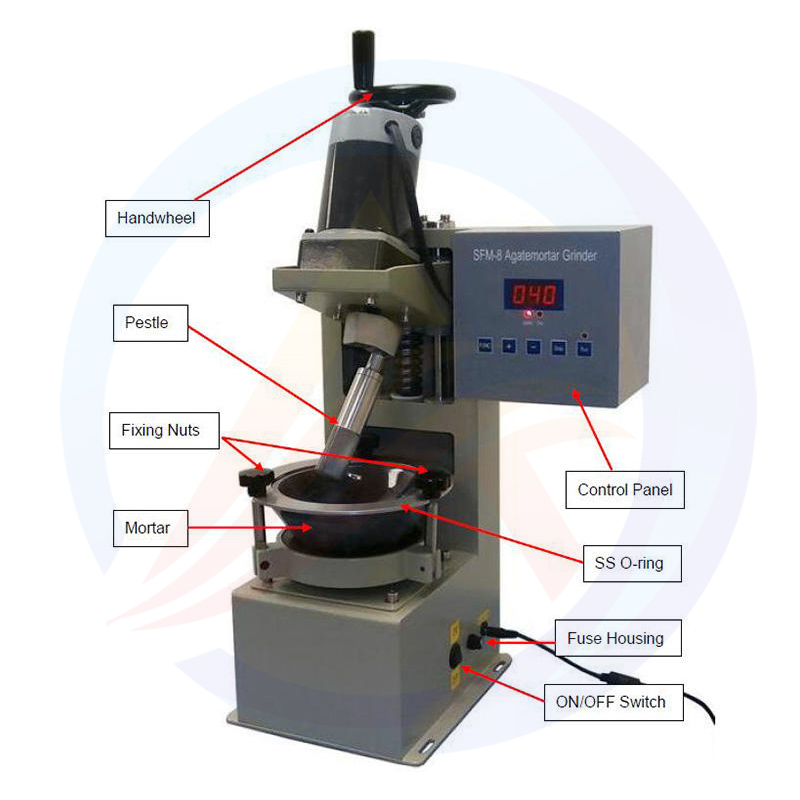
Vibrating Ball Mill three-dimensional pendulum ball mill for grinding and mixing of various materials.It is an ideal small equipment for laboratory preparation of ultrafine powder and nanomaterials.Dry and wet grinding can be used to mix solids, suspensions and pastes with different particles and materials. Grinding can be carried out in vacuum or inert gas.vibrating ball mill has the advantages of high efficiency, small size and light weight.
Working principle
Vibrating Ball Mill working principle of the Vibrating Ball Mill is to use a high-performance vibration motor to drive the entire grinding platform (usually equipped with multiple grinding jars) to perform high-speed, circular vibration in three-dimensional space. This complex motion causes the grinding balls (grinding balls) inside the grinding jar to produce intense energy collisions and friction.
Three dimensional motion: The grinding jar not only moves in the horizontal plane, but also in the vertical direction, ensuring that the grinding medium and sample move in all directions without dead corners inside the jar.
High frequency impact: Under the action of inertial force, the grinding ball impacts, shears, and grinds the sample material at extremely high speed and energy.
Efficient crushing: This high-energy collision can grind the sample to very fine particle size in a very short time.
Main product features and advantages
Efficient grinding, extremely fine particle size
With the high energy brought by three-dimensional vibration, Vibrating Ball Mill can quickly grind samples to the micrometer level (<10 um) or even nanometer level, making it an ideal choice for preparing ultrafine powders.
Grind evenly without any dead corners
The three-dimensional spatial motion ensures that the sample is thoroughly and uniformly mixed and ground, avoiding the problems of uneven or dead corners that may occur in traditional ball milling, and ensuring the consistency and representativeness of the sample.
Multiple material grinding jars to choose from
We usually offer grinding jars and grinding balls made of various materials such as stainless steel, agate, zirconia, polyurethane, polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), etc.
Advantages: Users can choose the most suitable grinding medium based on the characteristics of the sample, such as hardness, fear of metal contamination, and the need to maintain chemical purity, to avoid cross contamination. It is particularly suitable for fields with high purity requirements, such as lithium battery materials and pharmaceutical research and development.
Simultaneous operation of multiple jars, high efficiency and comparability
A host can usually hold 2, 4, or more grinding jars at the same time.
Advantages: Vibrating Ball Mill can process multiple identical or different samples simultaneously, greatly improving experimental efficiency and ensuring consistency in parallel experiments, making it easy to compare results.
Program control, intelligent operation
Adopting LCD display screen and programmable logic controller (PLC).
Advantages: Users can accurately set parameters such as grinding time, vibration frequency (or speed), pause interval (such as grinding cooling grinding to prevent sample overheating), etc. The experimental process is reproducible, the data is traceable, and meets the rigorous requirements of modern laboratories.
Safe and reliable
Usually equipped with a safety locking device to ensure that the grinding jar will not loosen during high-speed vibration, ensuring the safety of operators.
Design a well sealed grinding jar to prevent samples from escaping during the grinding process, especially suitable for grinding toxic or high-value samples. Some jars can also be filled with inert gas for protective grinding.
Low noise design
Compared to some large crushing equipment, vibration ball mills are usually designed to operate at lower noise levels and are more suitable for laboratory environments.
Typical application areas
This Vibrating Ball Mill is widely used in scientific research and quality inspection departments that require the preparation of fine powder samples:
Materials Science: Research and development of nanomaterials, ceramic materials, composite materials, metal powders, graphene, and positive and negative electrode materials for batteries (such as lithium iron phosphate and lithium cobalt oxide).
Geological metallurgy: Sample preparation before composition analysis of rocks, minerals, and ores.
Chemical engineering: preparation of catalysts, dispersion and mixing of pigments.
Life Sciences/Medicine: Grinding of plant tissues and medicinal materials, drug development.
Agriculture and Environmental Science: Analysis, Testing, and Pre treatment of Soil, Sediments, and Pollutants.