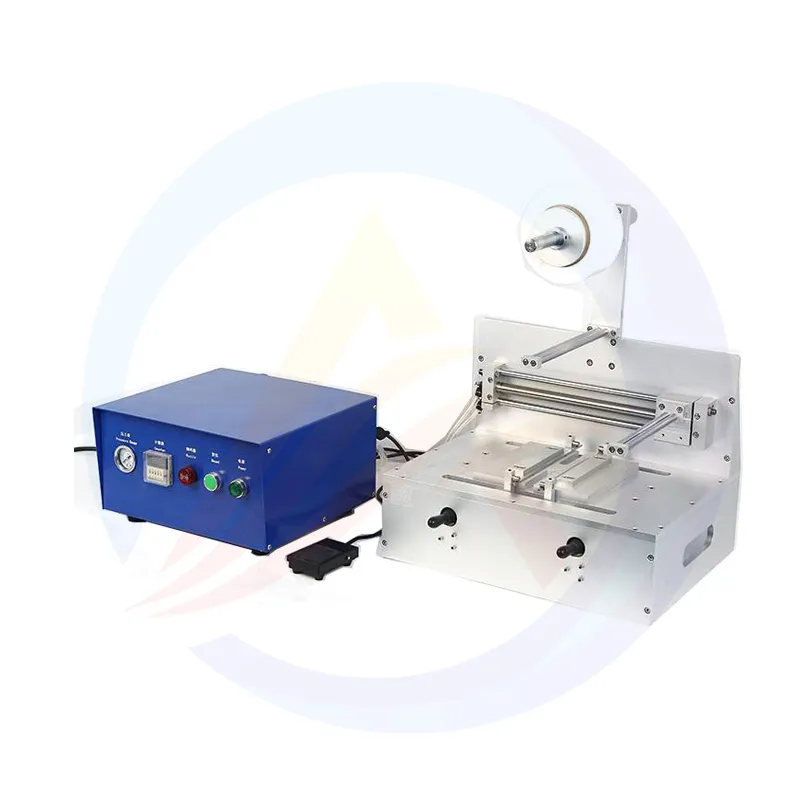
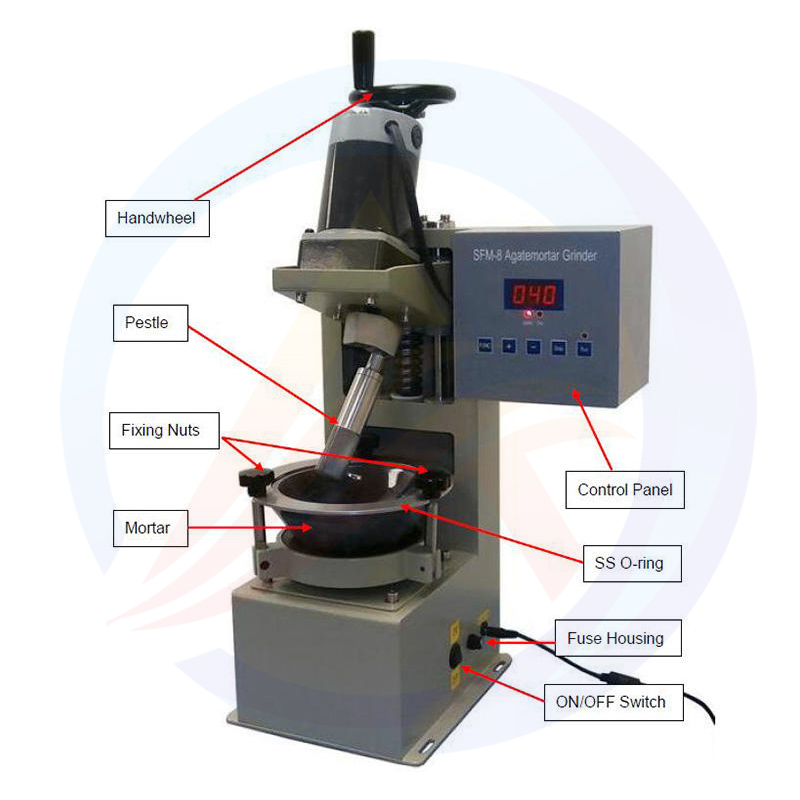
1. What is a lithium battery stacking equipment?
Lithium battery stacking equipment (also known as battery stacking machine) is the core automated equipment for manufacturing lithium-ion battery cells. Its core function is to precisely stack the positive electrode sheet, negative electrode sheet and separator in an alternating structure of "positive electrode - separator - negative electrode - separator", forming a dedicated device for the complete cell electrode group. Its core feature is to achieve the automated and high-precision stacking of electrode sheets and separators through mechanical structure, visual positioning, tension control and other technologies, replacing traditional manual operations and being a key component of the battery power production line.
2. The core functions of lithium battery stacking equipment
Precise stacking and forming: Through the visual positioning system (with an accuracy of ±0.05mm) and closed-loop control technology, ensure the alignment of electrode sheets and uniform wrapping of separators, form a structurally stable cell electrode group, avoid misalignment and missing sheets, etc.
Improving production efficiency: Achieve 24-hour continuous operation, with a single equipment daily output of 5,000-8,000 groups, which is 5-8 times higher than that of manual stacking (daily output less than 1,000 groups), supporting large-scale production.
Ensuring product consistency: Reduce errors caused by manual intervention, the product qualification rate has increased from less than 90% in manual stacking to over 99.5%, ensuring the uniform performance parameters of each cell group.
Adapting to diverse needs: Through modular design, it can switch electrode sheet sizes and stacking layers, adapt to various battery shapes such as form, pouch, and cylindrical, support the application of new materials (such as silicon-carbon negative electrode, high-nickel positive electrode).
3. Industry Impact of Lithium Battery Stack Equipment
Impact on Battery Performance: Directly determines the core indicators of the battery - if the alignment accuracy of the electrode sheets is less than 0.1mm, it will lead to an increase in internal resistance, a reduction in cycle life (up to 10%-15%), and even cause thermal runaway; high-precision stacking can increase the battery energy density by 5%-8% and extend the cycle life by 10%-15%.
Impact on Manufacturing Costs: Automation stacking reduces raw material loss and rework costs, while lowering labor costs, helping to reduce the cost of large-scale battery production and promoting the price reduction of new energy vehicles and energy storage products.
Impact on Industry Innovation: The high-speed and intelligent iteration of equipment (such as AI defect detection, application of digital twin technology) provides equipment support for the research and development of high-energy-density and long-cycle-life batteries, accelerating the industrialization process of new types of batteries.
Impact on Supply Chain: The process of domestic substitution of core components (such as high-precision vision sensors, linear motors) directly affects the autonomy and cost advantage of the domestic battery equipment industry chain.
4. Key Points for Scientific Selection of Battery Stackers
(1) Matching Production Requirements: Clarify Core Scene Positioning
Select based on battery type:
Square Battery power unit (mass production): Preferentially choose Z-type stackers with a stacking speed of 1200 pieces/hour or above, balancing efficiency and cost;
Soft-pack / Special-shaped batteries (high energy density requirements): Select laminated stackers, with ±0.05mm high precision to adapt to flexible current collectors and complex structures;
Multi-variety small-batch production: Choose mixed stackers, which can flexibly switch stacking modes and adapt to different product specifications.
Select based on production capacity:
Large-scale mass production (daily production capacity of 5000 units or more): Choose high-speed equipment (stacking speed of 1500 pieces/hour or above), with multi-station collaborative design;
Pilot / Small-batch production: Focus on equipment flexibility and easy debugging, without pursuing ultimate speed, prioritizing process compatibility.
(2) Focusing on Core Parameters: Quantify Technical Requirements
Precision indicators:Alignment accuracy of current collectors ≤ ±0.05mm, error in separator wrapping uniformity < 0.1mm, stacking pressure fluctuation range ≤ ±5% (directly affecting battery consistency);
Efficiency indicators:Reverse calculate the equipment stacking speed based on production capacity (e.g., daily production capacity of 8000 units requires a stacker with a speed of 1200 pieces/hour or above), while also paying attention to the stability of continuous operation of the equipment (fault rate lower than 0.5%);
Adaptability parameters: Range of current collector size (e.g., length 50-200mm, width 30-150mm), adjustment range of stacking layers, must cover the specifications of its own products; Compatibility of separator thickness (e.g., 12-25μm) and current collector thickness (e.g., 80-200μm).