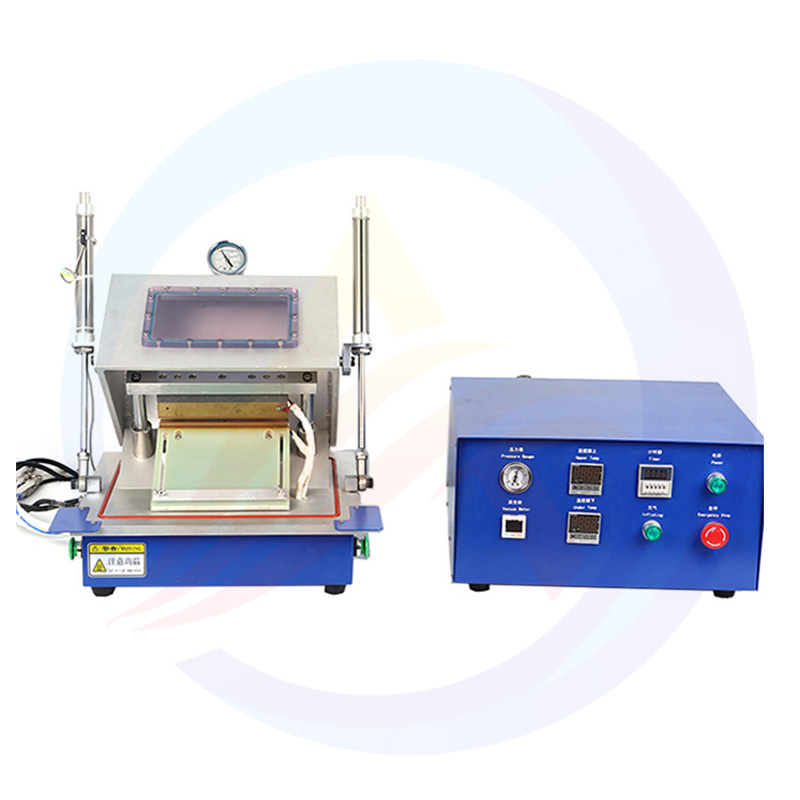
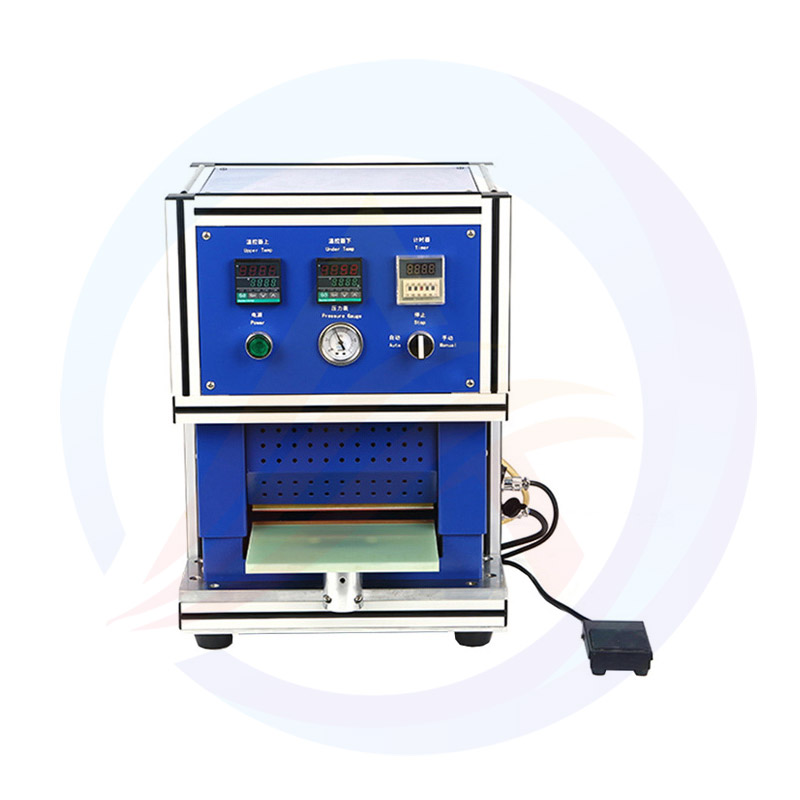
Battery Sealing Machines: Precision Engineering for the Energy Storage Revolution
Introduction
In the era of electrification, battery sealing machines have become indispensable in modern manufacturing facilities. These sophisticated systems play a crucial role in ensuring the safety, performance, and longevity of lithium-ion batteries that power our world. From smartphones to electric vehicles (EVs) and grid-scale energy storage, the quality of battery seals directly impacts product reliability and user safety.
1. Fundamental Principles of Battery Sealing
1.1 Sealing Objectives
- Maintain hermetic isolation of cell internals
- Prevent electrolyte leakage
- Control internal pressure
- Ensure electrical insulation
- Provide mechanical stability
1.2 Key Technical Requirements
- Leak rate: <10^-6 mbar·L/s (helium test)
- Burst pressure: >1.5 MPa
- Tensile strength: >20 N/mm
- Temperature resistance: -40°C to 85°C
- Cycle life: >1000 charge/discharge cycles
2. Core Components and Technologies
2.1 Mechanical Systems
- Precision alignment mechanisms
- Multi-axis motion control
- Force-controlled pressing systems
- Automated material handling
2.2 Sealing Methods
- Laser sealing
Wavelength: 1064nm (fiber) or 10.6μm (CO2)
Power range: 100W-1000W
Spot size: 0.1-0.5mm
- Ultrasonic sealing
Frequency: 20-40 kHz
Amplitude: 10-50 μm
Energy density: 50-200 J/cm²
- Thermal sealing
Temperature range: 150-300°C
Pressure: 0.5-2 MPa
Dwell time: 2-10 seconds
2.3 Quality Assurance Systems
- Helium mass spectrometry
- Machine vision inspection
- Pressure decay testing
- Electrical continuity check
3. Machine Architecture
3.1 Modular Design
- Loading/unloading stations
- Pre-treatment modules
- Sealing workcells
- Post-processing units
- Testing and sorting systems
3.2 Control Systems
- PLC-based sequence control
- HMI interfaces
- Data acquisition systems
- Remote monitoring capabilities
3.3 Material Handling
- Robotic arms (4-6 axis)
- Conveyor systems
- Precision fixturing
- Cleanroom-compatible designs
4. Process Capabilities
4.1 Production Capacity
- Throughput: 10-60 PPM (cells per minute)
- Uptime: >95%
- Changeover time: <30 minutes
- Yield rate: >99.5%
4.2 Flexibility
- Multiple cell formats
- Various material combinations
- Scalable production volumes
- Quick recipe changes
4.3 Precision Metrics
- Positioning accuracy: ±0.01mm
- Force control: ±0.1N
- Temperature control: ±0.5°C
- Seam width consistency: ±5%
5. Applications Across Industries
5.1 Consumer Electronics
- Smartphone batteries
- Laptop power cells
- Wearable device batteries
5.2 Electric Vehicles
- EV battery packs
- Hybrid vehicle batteries
- Charging station storage
5.3 Renewable Energy
- Grid-scale storage systems
- Home energy storage units
- Industrial backup power
5.4 Specialty Applications
- Medical device batteries
- Aerospace power systems
- Military-grade energy storage
6. Technological Advancements
6.1 Smart Manufacturing Integration
- IoT connectivity
- Predictive maintenance
- Digital twin simulations
- AI-driven process optimization
6.2 Advanced Materials Handling
- Dry room compatibility
- Inert gas environments
- Automated contamination control
6.3 Next-Generation Sealing Technologies
- Hybrid laser/ultrasonic methods
- Cold plasma surface treatment
- Nanomaterial-enhanced seals
- Solid-state battery adaptations
7. Selection and Implementation
7.1 Key Considerations
- Production volume requirements
- Cell format compatibility
- Quality standards compliance
- Total cost of ownership
- Supplier technical support
7.2 Implementation Process
- Facility assessment
- Process validation
- Operator training
- Production ramp-up
- Continuous improvement
8. Future Outlook
8.1 Market Trends
- Increasing automation levels
- Growing demand for flexible manufacturing
- Higher precision requirements
- Stricter safety regulations
8.2 Technological Developments
- AI-powered quality control
- Adaptive process control
- Sustainable manufacturing solutions
- Integration with battery R&D
8.3 Industry Challenges
- Material innovations
- Production scalability
- Cost reduction pressures
- Workforce development
Conclusion
Battery sealing machines represent a critical intersection of precision engineering, materials science, and advanced manufacturing. As the energy storage industry continues its rapid growth, these systems will play an increasingly vital role in enabling safer, more efficient, and more reliable batteries. Manufacturers must stay abreast of technological advancements and market trends to maintain competitiveness in this dynamic field.