Core functions and positioning
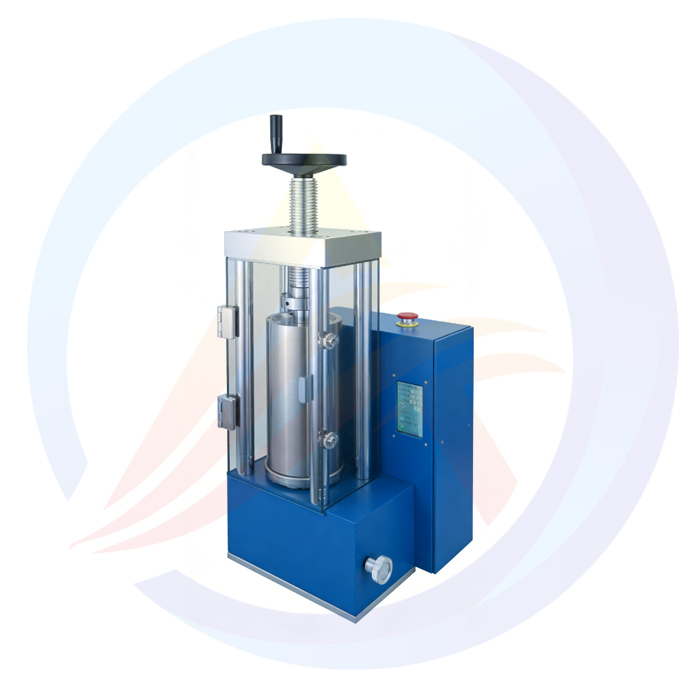
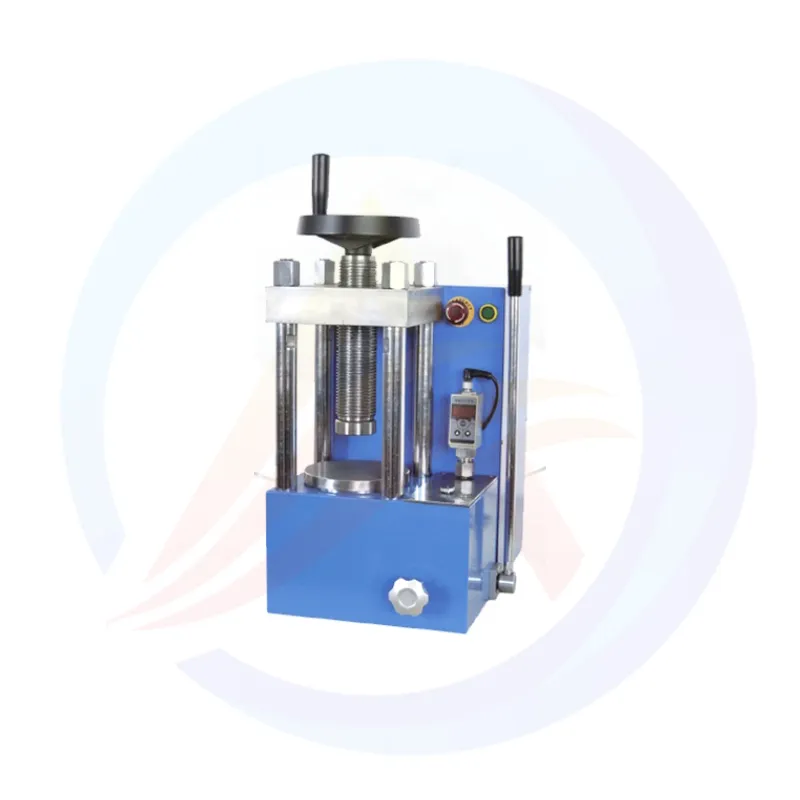
Core application: Laboratory Electric Pellet hydraulic press machine mainly used in laboratory environments to prepare solid tablets (tablets) or blocks by high-pressure compression of powder or granular materials (such as pharmaceutical powders, chemical raw materials, ceramic powders, metal powders, catalysts, food samples, etc.).
Core advantage: Provides adjustable and controllable high pressure (20-60 tons) to meet sample preparation requirements for different materials, densities, and hardness.
Laboratory Electric Pellet hydraulic press machine widely used in pharmaceutical research and development laboratories, chemical laboratories, materials research laboratories, university research institutes, quality inspection institutions, and other places where standardized test samples need to be prepared (such as for component analysis, strength testing, dissolution testing, spectral analysis, etc.).
Main advantage
Strong and adjustable pressure: covering a range of 20-60 tons, suitable for various material needs.
Relatively easy to operate (electric): more labor-saving and efficient than manual presses.
High sample consistency: Controllable pressure and holding function help prepare standardized samples with consistent density and thickness.
Widely applicable: Suitable for sample preparation in multiple fields such as pharmaceuticals, chemicals, materials, and scientific research.
Stable structure: The sturdy frame ensures long-term stable operation.
Safety: Equipped with necessary safety protection devices.
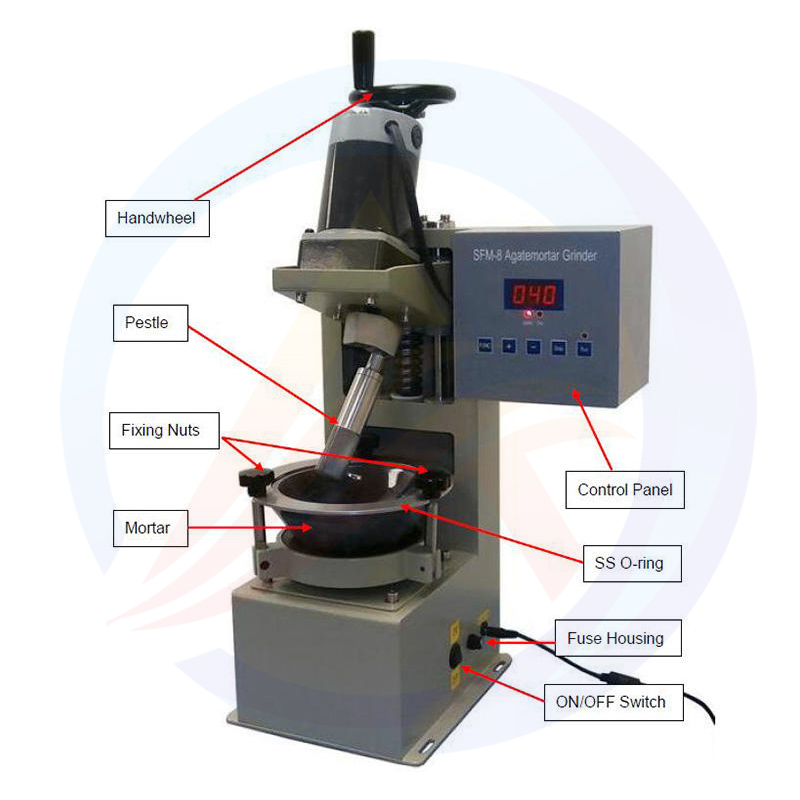
Key characteristics and components
Electric hydraulic system:
Power source: The hydraulic pump is driven by an electric motor, which is more labor-saving, efficient, and has more stable and controllable pressure compared to manual hydraulic presses.
Pressure generation: The hydraulic system converts electrical energy into hydraulic energy, driving the hydraulic cylinder to generate tremendous thrust.
Adjustable pressure range (20T-60T):
This is the most prominent feature of this model. Users can choose different tonnage models (such as 20 tons, 30 tons, 40 tons, 50 tons, 60 tons) based on the properties of the pressing material and the required density/hardness requirements of the sample. A larger tonnage can suppress materials that are harder or require higher density.
Stress framework:
A sturdy steel structure frame (usually C-shaped or H-shaped) is used to withstand the enormous pressure generated during the compression process, ensuring the rigidity and stability of the machine and preventing deformation.
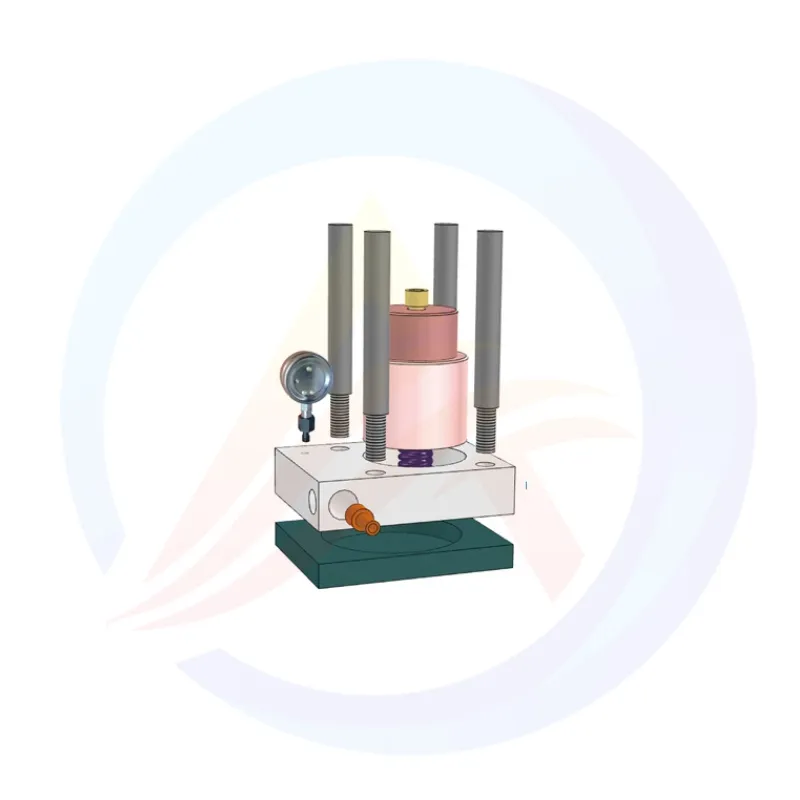
Hydraulic cylinder and pressure head:
Main hydraulic cylinder: the core component that generates downforce.
Up/down pressure head: a component that directly contacts the mold and material, usually made of high-strength steel. May be equipped with a heating device (optional) for materials that require hot pressing molding.
Workbench and mold:
Workbench: a platform for placing molds.
Mold: Core supporting components (usually purchased separately or customized). The mold determines the shape (circular, square, irregular, etc.) and size of the final tablet. The material of the mold (such as hard alloy, mold steel) should be selected according to the hardness of the pressing material.
Control system:
Pressure control: usually equipped with a pressure gauge or digital pressure gauge, which intuitively displays the current pressure. It may have pressure preset and holding function (setting target pressure and maintaining it for a period of time after reaching it), which is crucial to ensure consistency in sample density.
Travel control: Limited position devices may be used to control the stroke of the pressure head.
Operation: Control the rising, falling, stopping, and holding actions of the pressure head through buttons or switches. Some advanced models may be equipped with PLC and touch screen to achieve more precise program control.
Safety protection device:
Laboratory Electric Pellet hydraulic press machine usually includes safety barriers, protective covers, emergency stop buttons, overload protection valves, etc., to ensure the safety of operators and prevent overpressure damage to equipment.